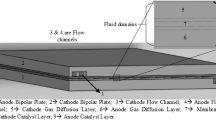
Abstract
Many efforts have been made to improve the performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). One approach has been the enhancement of the mass transport property by applying various channel designs and modifying them. Of those channels, the parallel channel as applied in PEMFCs has a low pressure drop and poor mass transfer property. To improve the mass transfer, a baffle that forces the reactant flow into the gas diffusion layer (GDL) from the channel can be installed in the parallel channel. In this study, various parallel channels designed with different baffle patterns and the effect was assessed by the PEMFC performance. All the baffle patterns analyzed in this study improved the performance of the PEMFC. However, depending on the baffle pattern, the reactant transfer and the current density of the PEMFC were affected differently. The staggered baffle pattern showed the best PEMFC performance among the analyzed models; when the staggered pattern was located near the outlet and the gap between the staggered baffles was wide, the PEMFC performance was further improved and the pressure drop of the cathode flow field was also lower than with the other baffle patterns.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Young-Beom Kim, upon reasonable request.
References
Hamilton, P. J., & Pollet, B. G. (2010). Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) flow field plate: design, materials and characterisation. Fuel Cells, 10(4), 489–509. https://doi.org/10.1002/fuce.201000033
Garraín, D., Lechón, Y., & Cdl, Rúa. (2011). Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) in automotive applications: environmental relevance of the manufacturing stage. Smart Grid and Renewable Energy. https://doi.org/10.4236/sgre.2011.22009
Moreno, N. G., Molina, M. C., & Gervasio, D. (2015). Approaches to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and their cost. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 52, 897–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.157
Saadi, A., Becherif, M., & Hissel, D. (2017). Dynamic modeling and experimental analysis of PEMFCs: a comparative study. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(2), 1544–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.07.180
Lu, X. Q., Qu, Y., Wang, Y. D., Qin, C., & Liu, G. (2018). A comprehensive review on hybrid power system for PEMFC-HEV: Issues and strategies. Energy Conversion and Management, 171, 1273–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.06.065.
Saco, S. A., Raj, R. T., & K.&Karthikeyan, P. (2016). A study on scaled up proton exchange membrane fuel cell with various flow channels for optimizing power output by effective water management using numerical technique. Energy, 113, 558–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.07.079.
Rostami, L., Nejad, P. M. G., & Vatani, A. (2016). A numerical investigation of serpentine flow channel with different bend sizes in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Energy, 97, 400–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.10.132.
Chowdhury, M. Z., & Timurkutluk, B. (2018). Transport phenomena of convergent and divergent serpentine flow fields for PEMFC. Energy, 161, 104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.143.
Chowdhury, M. Z., & Genc, O. (2018). Numerical optimization of channel to land width ratio for PEM fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43(23), 10798–10809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.149.
Rahimi-Esbo, M., Ranjbar, A. A., Ramiar, A., Alizadeh, E., & Aghaee, M. (2016). Improving PEM fuel cell performance and effective water removal by using a novel gas flow field. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(4), 3023–3037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.11.001.
Cooper, N. J., Smith, T., & Santamaria, A. D. (2016). Experimental optimization of parallel and interdigitated PEMFC flow-field channel geometry. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(2), 1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.11.153.
Liu, S. H., Chen, T., Xie, Y., Zhang, J. W., & Wu, C. Q. (2019). Numerical simulation and experimental study on the effect of symmetric and asymmetric bionic flow channels on PEMFC performance under gravity. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(56), 29618–29630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.06.046.
Kang, H. C., Jum, K. M., & Sohn, Y. J. (2019). Performance of unit PEM fuel cells with a leaf-vein-simulating flow field-patterned bipolar plate. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(43), 24036–24042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.120.
Atyabi, S. A., & Afshari, E. (2019). Three-dimensional multiphase model of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with honeycomb flow field at the cathode side. Journal of Cleaner Production, 214, 738–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.293.
Wen, D. H., Yin, L. Z., Piao, Z. Y., Lu, C. D., & Li, G. (2018). Performance investigation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with intersectant flow field. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 121, 775–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.01.053.
Zhang, G. B., Xie, B., Bao, Z. M., Niu, Z. Q., & Jiao, K. (2018). Multi-phase simulation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with 3D fine mesh flow field. International Journal of Energy Research, 42(15), 4697–4709. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4215.
Bao, Z. M., Niu, Z. Q., & Jiao, K. (2019). Analysis of single- and two-phase flow characteristics of 3-D fine mesh flow field of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 438, 226995.
Niu, Z. Q., Fan, L. H., Bao, Z. M., & Jiao, K. (2018). Numerical investigation of innovative 3D cathode flow channel in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. International Journal of Energy Research, 42(10), 3328–3338. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4086
Perng, S. W., Wu, H. W., Chen, Y. B., & Zeng, Y. K. (2019). Performance enhancement of a high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell by bottomed-baffles in bipolar-plate channels. Applied Energy, 255, 113815.
Wu, H. W. (2011). The optimal parameters estimation for rectangular cylinders installed transversely in the flow channel of PEMFC from a three-dimensional PEMFC model and the Taguchi method. Applied Energy, 88(12), 4879–4890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.06.034.
Liu, H. C., Yan, W. M., Soong, C. Y., & Chen, F. L. (2005). Effects of baffle-blocked flow channel on reactant transport and cell performance of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 142(1–2), 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.09.037.
Heidary, H., Kermani, M. J., & Dabir, B. (2016). Influences of bipolar plate channel blockages on PEM fuel cell performances. Energy Conversion and Management, 124, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.06.043.
Yin, Y., Wang, X. F., Xiang, S. G., Zhang, J. F., & Qin, Y. Z. (2018). Numerical investigation on the characteristics of mass transport and performance of PEMFC with baffle plates installed in the flow channel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43(16), 8048–8062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.037.
Yin, Y., Wang, X. F., Zhang, J. F., Xiang, S. G., & Qin, Y. Z. (2019). Influence of sloping baffle plates on the mass transport and performance of PEMFC. International Journal of Energy Research, 43(7), 2643–2655. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4306.
Zhang, G. B., Fan, L. H., Sun, J., & Jiao, K. (2017). A 3D model of PEMFC considering detailed multiphase flow and anisotropic transport properties. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 115, 714–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.07.102.
Wang, B. W., Chen, W. M., Pan, F. W., Wu, S. Y., Zhang, G. B., Park, J. W., Xie, B., Yin, Y., & Jiao, K. (2019). A dot matrix and sloping baffle cathode flow field of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 434, 226741.
Perng, S. W., & Wu, H. W. (2015). A three-dimensional numerical investigation of trapezoid baffles effect on non-isothermal reactant transport and cell net power in a PEMFC. Applied Energy, 143, 81–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.059.
Houreh, N. B., Shokouhmand, H., & Afshari, E. (2019). Effect of inserting obstacles in flow field on a membrane humidifier performance for PEMFC application: A CFD model. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(57), 30420–30439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.189.
Guo, H., Chen, H., & Ye, F. (2019). Baffle shape effects on mass transfer and power loss of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with different baffled flow channels. International Journal of Energy Research, 43(7), 2737–2755. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4328.
Perng, S. W. (2011). Non-isothermal transport phenomenon and cell performance of a cathodic PEM fuel cell with a baffle plate in a tapered channel. Applied Energy, 88(1), 52–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.07.006.
Li, W. K., Zhang, Q. L., Wang, C., Yan, X. H., Shen, S. Y., Xia, G. F., Zhu, F. J., & Zhang, J. L. (2017). Experimental and numerical analysis of a three-dimensional flow field for PEMFCs. Applied Energy, 195, 278–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.008.
Sun, F., Su, D. D., Yin, Y. J., & Pang, B. (2022). Effects of combined baffles on the proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance. International Journal of Electrochemical Science. https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.11.18
Huang, Y., Song, J. N., Deng, X. Y., Chen, S., Zhang, X., Ma, Z. P., Chen, L. J., & Wu, Y. L. (2023). Numerical investigation of baffle shape effects on performance and mass transfer of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126448
Liu, Q., Lan, F., Chen, J., Wang, J., & Zeng, C. (2022). Flow field structure design modification with helical baffle for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energy Conversion and Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.116175
Zhang, S. Y., Qu, Z. G., Xu, H. T., Talkhoncheh, F. K., Liu, S., & Gao, Q. (2021). A numerical study on the performance of PEMFC with wedge-shaped fins in the cathode channel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(54), 27700–27708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.05.207.
Cai, Y. H., Sun, J. M., Wei, F., & Chen, B. (2022). Effect of baffle dimensionless size factor on the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103812
Heidary, H., Kermani, M. J., Advani, S. G., & Prasad, A. K. (2016). Experimental investigation of in-line and staggered blockages in parallel flowfield channels of PEM fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(16), 6885–6893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.028.
Wang, X. F., Qin, Y. Z., Wu, S. Y., Xiang, S. G., Zhang, J. F., & Yin, Y. (2020). Numerical and experimental investigation of baffle plate arrangement on proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance. Journal of Power Sources. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228034
Gostick, J. T., Fowler, M. W., Pritzker, M. D., & Ioannidis, M. A. (2006). In-plane and through-plane gas permeability of carbon fiber electrode backing layers. Journal of Power Sources, 162(1), 228–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.096.
Zhang, Z. Q., & Liu, W. (2019). Three dimensional two-phase and non-isothermal numerical simulation of multi-channels PEMFC. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(1), 379–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.05.149.
Li, S., Yuan, J. L., Andersson, M., Xie, G. N., & Sunden, B. (2017). Influence of anisotropic gas diffusion layers on transport phenomena in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. International Journal of Energy Research, 41(14), 2034–2050. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.3763.
Khajeh-Hosseini-Dalasm, N., Kermani, M. J., Moghaddam, D. G., & Stockie, J. M. (2010). A parametric study of cathode catalyst layer structural parameters on the performance of a PEM fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(6), 2417–2427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.12.111.
Li, W. Z., Yang, W. W., Zhang, W. Y., Qu, Z. G., & He, Y. L. (2019). Three-dimensional modeling of a PEMFC with serpentine flow field incorporating the impacts of electrode inhomogeneous compression deformation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(39), 22194–22209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.06.187.
Yang, X. G., & Ye, Q. (2011). Matching of water and temperature fields in proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform distributions. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36(19), 12524–12537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.07.014.
Lampinen, M. J., & Fomino, M. (1993). Analysis of free-energy and entropy changes for half-cell reactions. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 140(12), 3537–3546. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2221123
Jiao, K., & Li, X. G. (2011). Water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 37(3), 221–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2010.06.002
Ye, Q. (2007). Three-dimensional simulation of liquid water distribution in a PEMFC with experimentally measured capillary functions. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 154(12), B1242–B1251. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2783775
Meng, H. (2010). Numerical studies of liquid water behaviors in PEM fuel cell cathode considering transport across different porous layers. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35(11), 5569–5579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.03.073.
Um, S., & Wang, C. Y. (2000). Computational fluid dynamics modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 147(12), 4485–4493. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1394090
Springer, T. E., Zawodzinski, T. A., & Gottesfeld, S. (1991). Polymer electrolyte fuel-cell model. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 138(8), 2334–2342. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2085971
Zawodzinski, T. A., Springer, T. E., Uribe, F., & Gottesfeld, S. (1993). Characterization of Polymer Electrolytes for fuel-cell applications. Solid State Ionics, 60(1–3), 199–211. Doi 10.1016/0167–2738(93)90295-E.
Tomadakis, M. M., & Robertson, T. J. (2005). Viscous permeability of random fiber structures: Comparison of electrical and diffusional estimates with experimental and analytical results. Journal of Composite Materials, 39(2), 163–188. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998305046438.
Yan, Q. G., Toghiani, H., & Causey, H. (2006). Steady state and dynamic performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) under various operating conditions and load changes. Journal of Power Sources, 161(1), 492–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.03.077.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning(KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government(MOTIE)(20212020800090, Development and Demonstration of Energy-Efficiency Enhanced Technology for Temperature-Controlled Transportation and Logistics Center) and the Korean National Research Foundation (No.NRF-2021R1A2C2013203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Son, J., Um, S. & Kim, YB. Effect of Baffle Pattern Applied to Cathode Parallel Channel on PEMFC Performance. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 11, 145–159 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-023-00534-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-023-00534-3